What is Drag?
Drag is the resistance that water exerts on your body as you move through it. There are two phases of drag, known as passive drag and active drag. Passive drag is the resistance a swimmer meets while swimming forward. Active drag is the resistance a swimmer exerts.
There are three main types of water resistance that affect swimmers:
Elite swimmers are always striving to reduce as much drag as possible. By cutting down drag, swimmers not only give themselves opportunities to swim faster, but also learn how to swim more efficiently.
There are three main types of water resistance that affect swimmers:
- Form resistance: the water resistance is dependent on your body position
- Wave resistance: the resistance caused by turbulence at the water surface
- Friction resistance: the resistance caused by contact of skin and hair in water
Elite swimmers are always striving to reduce as much drag as possible. By cutting down drag, swimmers not only give themselves opportunities to swim faster, but also learn how to swim more efficiently.
How Do You Reduce Drag?
 Speedo's LZR Racer suit
Speedo's LZR Racer suit
Many swimmers turn to things like swimsuits and caps in order to reduce drag. It is not completely proven whether or not Speedo LZR Racers and body suits are directly correlated with time drops. However, Olympians and elite swimmers are constantly testing out different fast suits, and many have broken records wearing them. Already, the Speedo LZR Racer suit has assisted in setting 38 new world records by 2008.
In scientific terms, fast suits are meant to cut down passive drag and make the water pushing past the swimmer's body travel more smoothly. They compress and streamline the swimmer's body, while allowing the muscles to work more efficiently. They also have "internal core stabilizers" that help swimmers stay in the best body position even as they become tired. In addition, most fast suits are made of water-repellent fabric.
Caps are also known to help with drag reduction. Most swimmers wear caps to reduce friction and resistance, making a smoother surface on their heads. Swimmers usually use either latex caps or silicone caps. They both work the same way, but have their differences: latex caps are thinner and prone to ripping, but less expensive; silicone caps are sleeker and thicker with less wrinkles, but more expensive than latex caps.
In scientific terms, fast suits are meant to cut down passive drag and make the water pushing past the swimmer's body travel more smoothly. They compress and streamline the swimmer's body, while allowing the muscles to work more efficiently. They also have "internal core stabilizers" that help swimmers stay in the best body position even as they become tired. In addition, most fast suits are made of water-repellent fabric.
Caps are also known to help with drag reduction. Most swimmers wear caps to reduce friction and resistance, making a smoother surface on their heads. Swimmers usually use either latex caps or silicone caps. They both work the same way, but have their differences: latex caps are thinner and prone to ripping, but less expensive; silicone caps are sleeker and thicker with less wrinkles, but more expensive than latex caps.
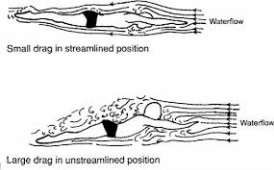 Drag forces and streamlining
Drag forces and streamlining
In addition to swimsuits and caps, swimmers can also reduce drag by having better technique.
For example, streamlining can have a significant effect on drag reduction. According to scientific research and data, streamlining helps minimize the surface area traveling through water, which increases speed.
For example, streamlining can have a significant effect on drag reduction. According to scientific research and data, streamlining helps minimize the surface area traveling through water, which increases speed.
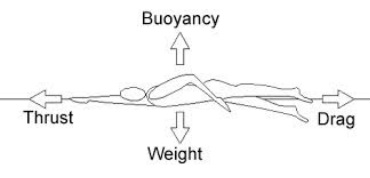 Forces in swimming
Forces in swimming
In scientific terms, you could also take buoyancy under consideration.
Water is 1000 times more resistant than air; you will see this when you try to walk across a swimming pool normally, as you would walk on land. In fact, a person loses about 91% of his/her energy in water.
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted on submerged objects. It acts on swimmers, too, explaining why they float while swimming. Along with the fact that humans are less dense than water, their weight is usually lighter than or equal to the buoyant force acting on them, allowing them to float.
Swimmers aim to be buoyant and try to keep close to the surface. The water at the surface of water is less resistant than the water below. To maintain their buoyancy, swimmers should keep their hips and shoulders level by slightly pressing their upper body down. The upper body is naturally more buoyant than the lower, because pressure spreads out more thinly on it due to its greater surface area. By being more buoyant, swimmers can swim on the surface of the water, thus swimming through less resistant water.
Water is 1000 times more resistant than air; you will see this when you try to walk across a swimming pool normally, as you would walk on land. In fact, a person loses about 91% of his/her energy in water.
Buoyancy is the upward force exerted on submerged objects. It acts on swimmers, too, explaining why they float while swimming. Along with the fact that humans are less dense than water, their weight is usually lighter than or equal to the buoyant force acting on them, allowing them to float.
Swimmers aim to be buoyant and try to keep close to the surface. The water at the surface of water is less resistant than the water below. To maintain their buoyancy, swimmers should keep their hips and shoulders level by slightly pressing their upper body down. The upper body is naturally more buoyant than the lower, because pressure spreads out more thinly on it due to its greater surface area. By being more buoyant, swimmers can swim on the surface of the water, thus swimming through less resistant water.
